How Does Water Move Through Nonvascular Plants?
In non-vascular plants some plants absorb the nutrients directly from the environment and some have thin rootlike structures known as rhizoids that absorb water and nutrients through the soil and they are transported to each cell through the thin cell walls although this is much slower than vascular. Habitats of these plants are swamps bogs or near water sources.

Plants By James Nguyen Source: www.haikudeck.com
How do these trees grow so tall.

How does water move through nonvascular plants?. Nonvascular plants are usually found growing close to. Bryophytes an informal group that taxonomists now. Non-vascular plants include two distantly related groups.
Tube-like structures that move water through vascular plants. Flow Δψ R which is analogous to electron flow in an electrical circuit described by Ohms law equation. Redwood trees found in Yosemite National Park in California.
They are generally small plants limited in size by poor transport methods for water gases and other compounds. This means that they are. Nonvascular Plants Nonvascular plants are plants that do not have any special internal pipelines or channels to carry water and nutrients.
Classification of Seedless Vascular Plants The other line of lycophytes are small nonwoody plants. Nonvascular plants are commonly found in moist environments so that they are always close to a water source and can absorb the water right into the main part of the plant without relying on roots. Water moves into the roots of a plant through osmosis.
1 point tube-like structures that move water through nonvascular plants. Plant Structure Quick Check What is xylem. The relative ease with which water moves through a part of the plant is expressed quantitatively using the following equation.
They reproduce via spores rather than seeds and do not produce flowers fruit or wood. How does water move from the roots to the top of these trees. Since nonvascular plants lack water-conducting tissues these plants cannot grow high.
Tube-like structures that move food through nonvascular plants. Tube-like Grade 8 SCIENCE. Beside above what happens when you put a stalk of celery in colored water.
Also these plants cannot tolerate drought. When water moves through the stem it contains nutrients and minerals the plant needs to survive. But they can absorb water from the surrounding air or nearby sources through surface tissues.
Where do seedless nonvascular plants live. Observing Water Movement Within Celery In plants water moves up from the roots through the stem and into the branches and leaves. I V R where R is the resistance i is the current or flow of electrons and V is the voltage.
A non-vascular plant has no specialized conducting tissues so it usually depends on simple osmosis to move fluids from areas of high water. In here the water-rich soil has a high water concentration while the roots have low water concentration. The non-vascular plants include mosses hornworts and liverworts and some algae.
These plants depend on diffusion and osmosis for their water supply. What is xylem. Instead nonvascular plants absorb water and minerals directly through their leaflike scales.
It has a lot to do with a very efficient system to move water sugars and other nutrients. Osmosis is the net movement of solvent molecules down a concentration gradient through a partially permeable membrane. When you water plants the plants leaves absorb the water so that the water goes in the plant and then when it gets into the plant it goes through the root system which the water is going down.
Instead they may possess simpler tissues that have specialized functions for the internal transport of water. In the plant system Vis equivalent to the water. But the first plants to have such a vascular system were not tall trees but much smaller plants.
In vascular plants the nutrients are created in the leaves and transported by the phloem. Non-vascular plants are plants without a vascular system consisting of xylem and phloem. Tube-like structures that move water through vascular plants.
Non-vascular plants tend to be small due to the lack of a vascular tissue to transport water. Water Moves through a plant by its leaf. Tube-like structures that move food through nonvascular plants.
1 point tube-like structures that move water through nonvascular plants.

Non Vascular Plants Basic Biology Source: basicbiology.net

Nonvascular Plants Youtube Source: www.youtube.com
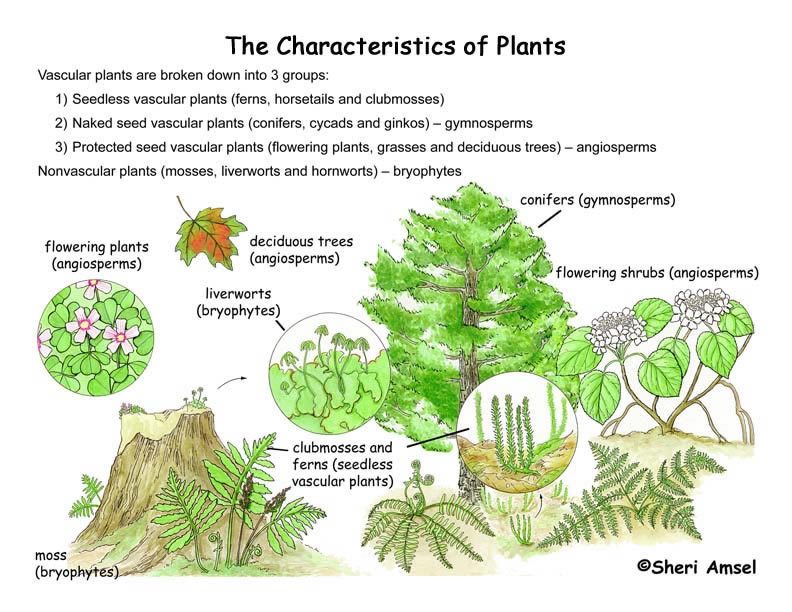
Vascular Plants Vs Nonvascular Plants Source: www.exploringnature.org
6 L 5b 1 How Vascular Nonvascular Transport Food Water South Carolina 6th Grade Science Source: sc6thgradescience.weebly.com
Nonvascular Plants Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation Source: www.ck12.org

Non Vascular Plants Basic Biology Source: basicbiology.net

