Describe A Monohybrid Cross Of Plants
Monohybrid Test Cross Practice WS 1A Name. Homozygous recessive ss plants have dented seeds.
Monohybrid Crosses Objective Ppt Video Online Download Source: slideplayer.com
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits is called a monohybrid cross.
Describe a monohybrid cross of plants. Pollen from true-breeding pea plants with purple flowers one trait was placed on stigmas of true-breeding. As in a dihybrid cross the F1 generation plants produced from a monohybrid cross are heterozygous and only the dominant phenotype is observed. If a cross is made between two plants or animals having a pair of contrasting characters the genes lie side by side without being blended and pass to different gametes after being separated during the formation of gametes.
Punnett square analysis can be used to predict the genotypes of the F2 generation. The garden pea was good choice of experimental organism because many varieties were available that bred true. WBateson was the first one to coin the term genetics in 1905.
However each parent possesses different alleles for that particular trait. Mendels monohybrid cross - definition Mendel crossed true-breeding plants that differed for a given character A monohybrid cross involves one mono character and different hybrid traits. Describe the following monohybrid cross of plants.
Experimenter can cross cross-pollinate any two pea plants at will. F2 3 of the 4 plants are tall and 1 is short. Transfer of pollen between plants that vary in only one trait.
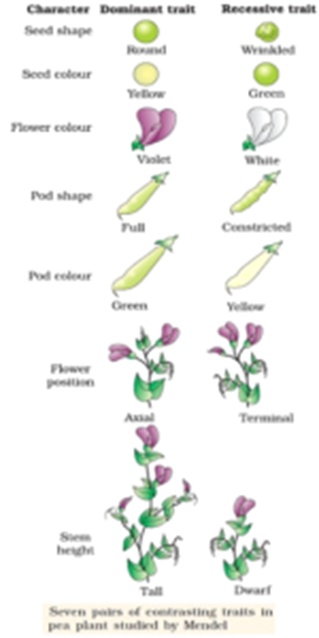
The phenotypic ratio of the resulting F2 generation is 31. The procedure is as follows. Mendel performed seven types of monohybrid crosses each involving contrasting traits for different characteristics.
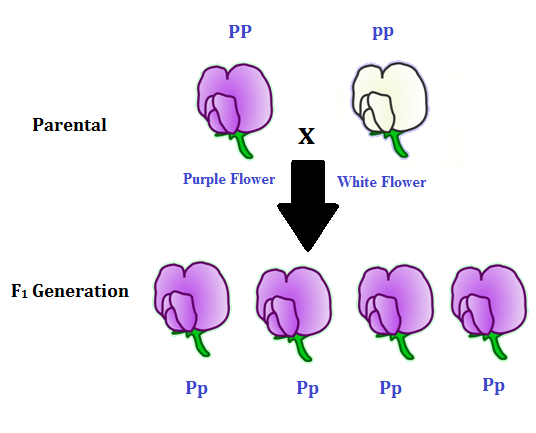
Describe a monohybrid cross of plants. When fertilization occurs between two true-breeding parents that differ by only the characteristic being studied the process is called a monohybrid cross and the resulting offspring are called monohybrids. A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between P generation parental generation organisms that differ in a single given trait.
We will then examine ears of corn Purple results from the dominant allele P and yellow from the recessive allele p. A cross between two pure homozygous patterns in which the inheritance pattern of only one of contrasting characters is studied is called monohybrid cross. Here the example is used of stem height in pea plants.
In this activity you will practice with one trait crosses monohybrid as well as test crosses. Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 was an Austrian monk who discovered the basic rules of inheritance. First we will use Punnett square diagrams to predict the results of various monohybrid crosses.
The anthers from one plant are removed before they have opened to shed their pollen an operation called emasculation that is done to prevent selfing. The P generation organisms are homozygous for the given trait. About 34 exhibit the dominant phenotype and 14 exhibit the recessive phenotype.
A cross between two types of plants of same species considering only the transmission of one character is called monohybrid cross. Presence of the dominant allele S in homozygous SS or heterozygous Ss plants results in spherical seeds. A monohybrid cross is one that involves only one trait.
___ Honors Biology I Introduction to Genetics Honor Pledge. _____ Honors Biology Introduction to Genetics Objective. It is a cross between two pure obtained by true breeding parents differing in a single pair of contrasting characters.
From 1858 to 1866 he bred garden peas in his monastery garden and analyzed the offspring of these matings. Each species has similarities among themselves due to the cause of heredity. Both parent plants are heterozygous Ss for an allele that determines seed shape.
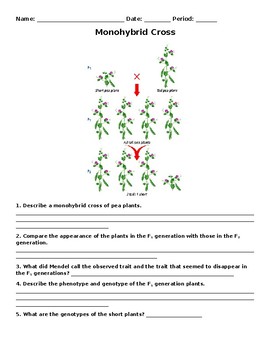
Punnett square analysis of a monohytbrid cross. Use the following diagram to answer questions 1-5. In this activity you will practice with one trait crosses monohybrid as well as test crosses.
Use the following diagram to answer questions 1-5. Monohybrid Test Cross Practice WS 1A Name. LIKE BEGETS LIKE which means young one resemble their parents MONOHYBRID CROSS DIHYBRID CROSS is the well-known dogma associated with heredity.
F1 is all Tall. Tall plants are dominant to dwarf plants th. Pollen from the other plant is then transferred to the receptive stigma with a paintbrush or on anthers themselves.
The figure above represents a monohybrid cross of F1-hybrid plants. For example a cross between tall pea plants and dwarf pea plant that is considering only the height of the parents is a monohybrid cross. Compare the appearance of the plants in the F1 generation with those in the F2 generation.
This cross produces F1 heterozygotes with a yellow phenotype. Describe the following monohybrid cross of plants. It is derived from the greek word genesis means to grow into or to become.
In the P generation pea plants that are true-breeding for the dominant yellow phenotype are crossed with plants with the recessive green phenotype.

Monohybrid Cross Mendel S Experiment Procedure Conclusion Source: thefactfactor.com

4 2 1 Monohybrid Crosses And Segregation Biology Libretexts Source: bio.libretexts.org
Monohybrid Cross Questions By Free Teacher Stuff Tpt Source: www.teacherspayteachers.com
Overview On Monohybrid Cross Definition Example Source: byjus.com
Monohybrid Crosses Bioninja Source: www.vce.bioninja.com.au

12 2c The Punnett Square Approach For A Monohybrid Cross Biology Libretexts Source: bio.libretexts.org
